Cell type prediction with CellKb
Annotating individual cells in the PBMC dataset with CellKb and comparing with SingleR
January 11, 2024
Ajay Patil
In this article, we use CellKb to assign cell types to individual cells in the dataset of Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells (PBMC) freely available from 10X Genomics.
There are 2,700 single cells that were sequenced on the Illumina NextSeq 500.
The raw data can be found here.
This is the same dataset analyzed in the Scanpy and Seurat clustering tutorials.
Annotating cells individually is more likely to identify rare cell types and give a better prediction when the clusters identified in your dataset are not cleanly separated.
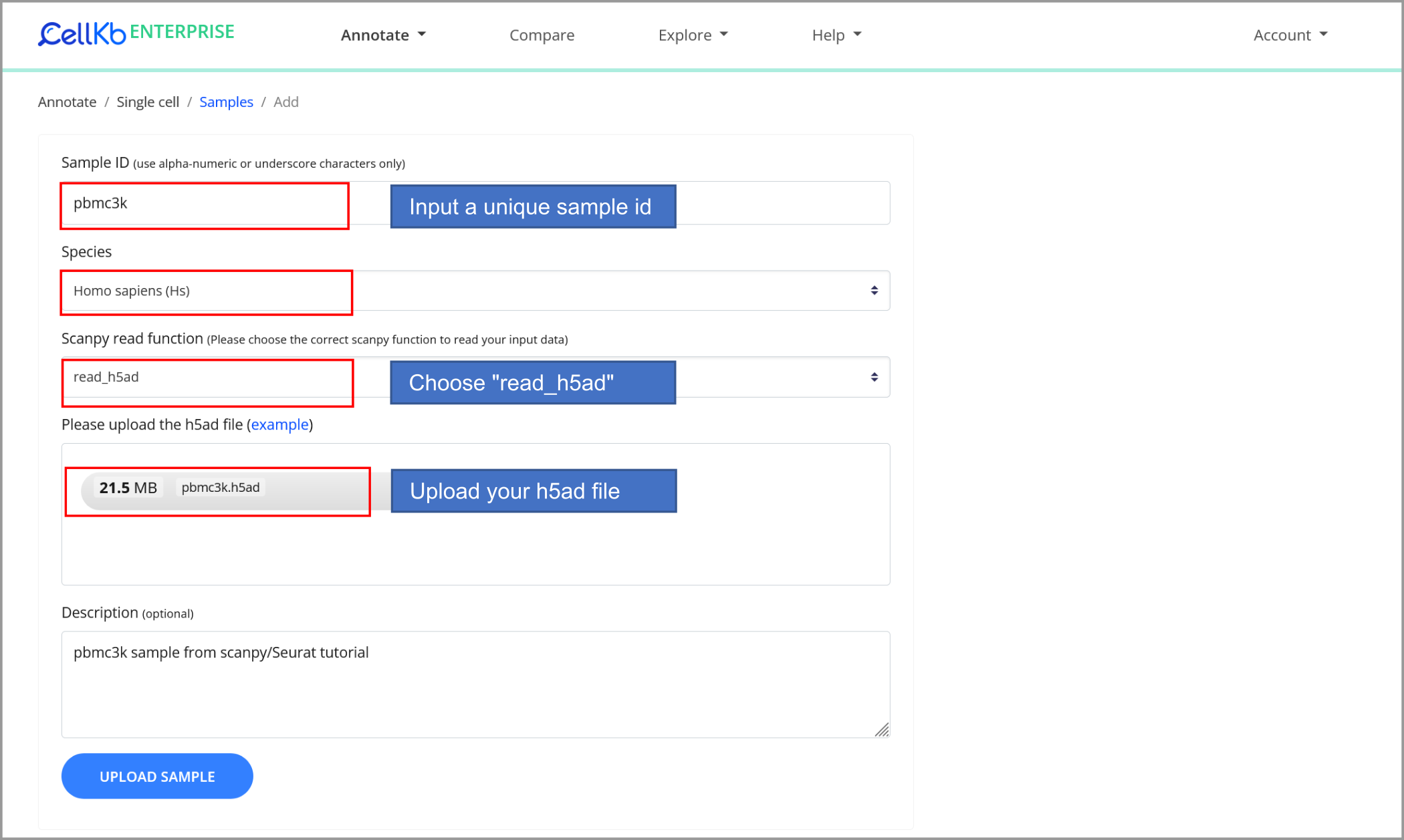
Upload the dataset to CellKb
We upload the dataset to CellKb. CellKb uses Scanpy for reading/pre-processing the dataset.
Support for annotation of cells in Seurat objects will be added in the future.
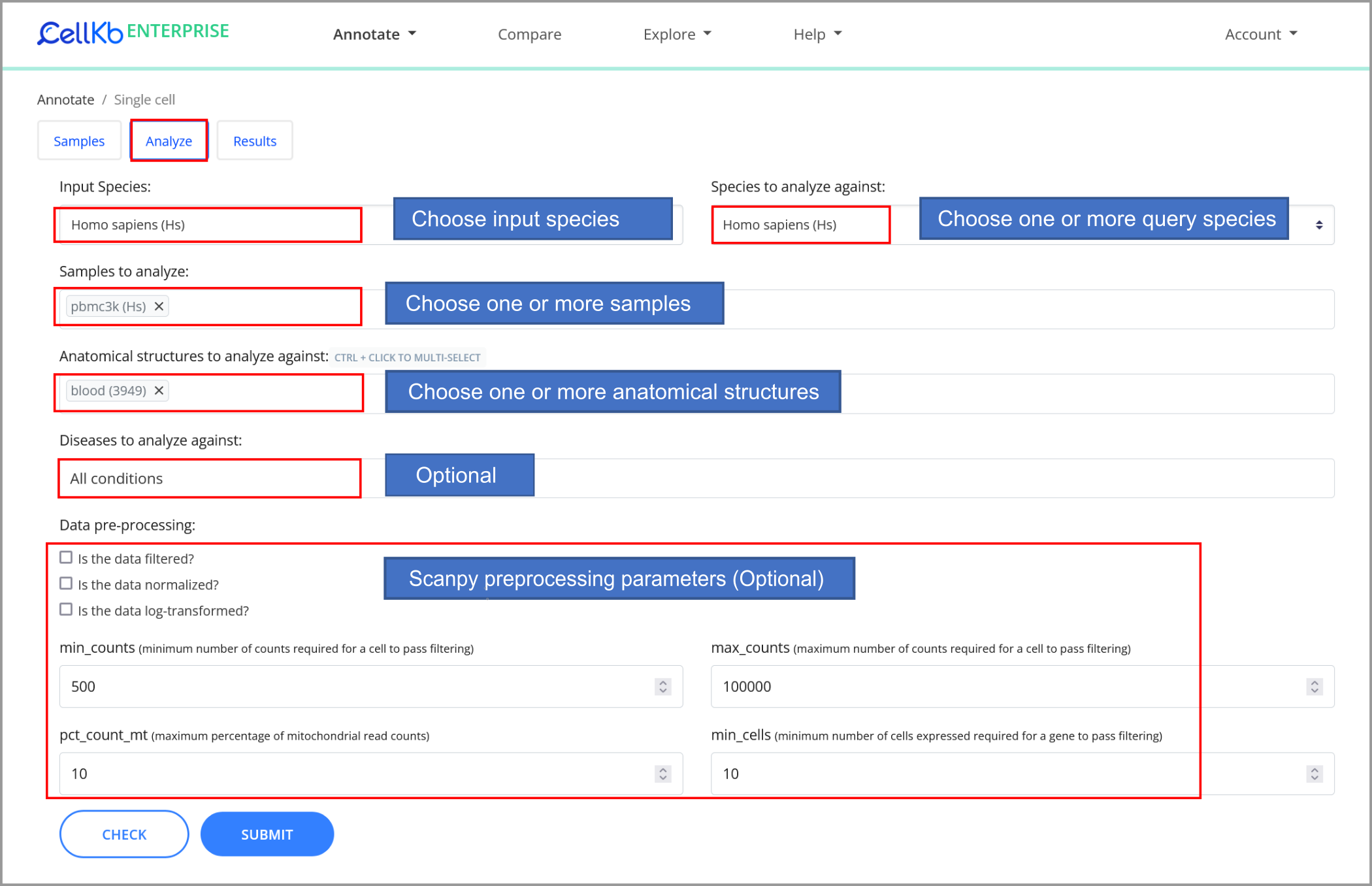
Analyze the dataset
We can now submit the dataset for single-cell annotation, choosing "Blood" in the filter criteria.
Download results
The analysis runs in the background, and you can check the status on the "Results" screen.
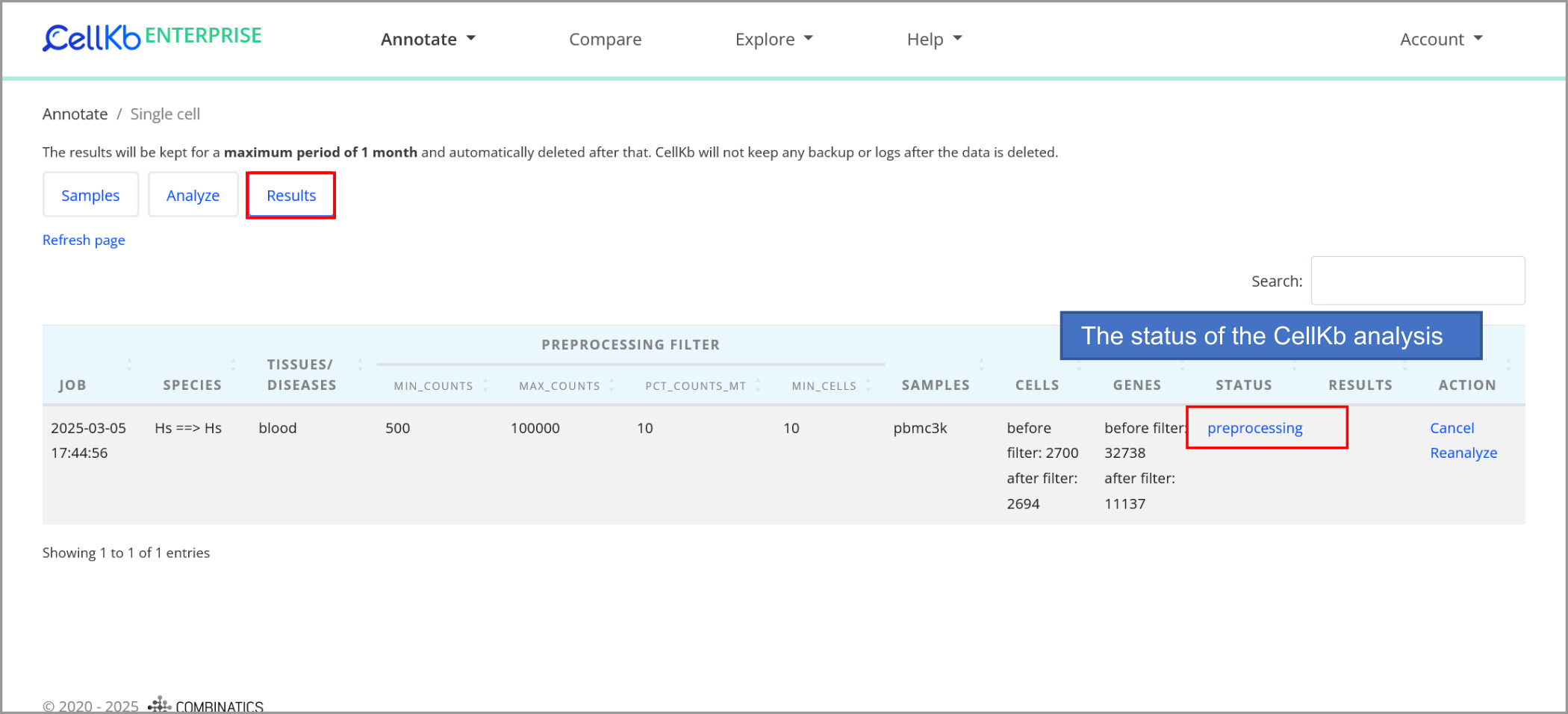
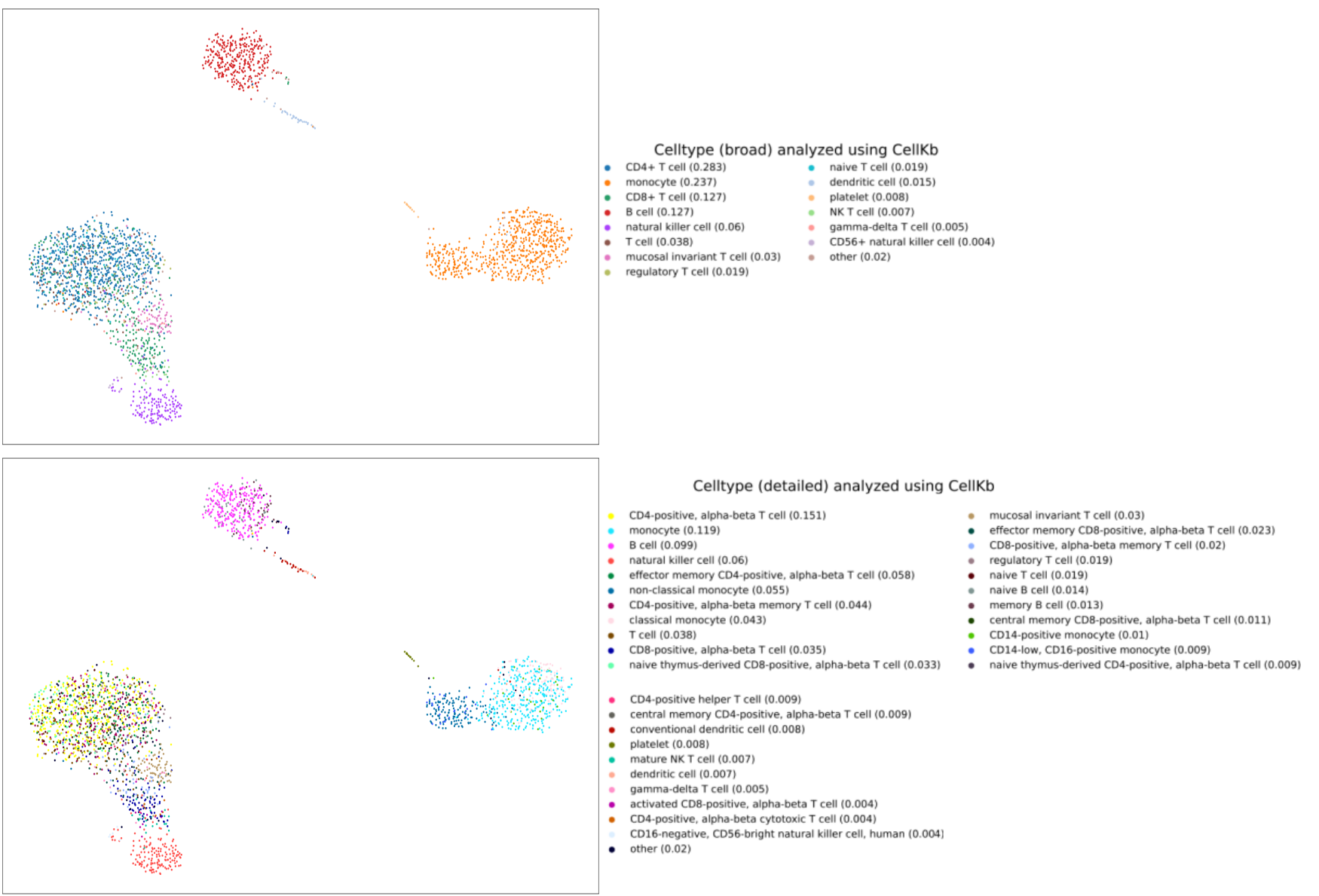
After the analysis is complete, you can download the results. The results contain TSV file and PDF files with one plot for each cell type identified,
and a summary plot with the broad and detailed cell types identified. We show the summary plot for the pbmc3K dataset here.
Analyzing the pbmc3k dataset using SingleR
We analyze the same pbmc3k dataset using SingleR with the HumanPrimaryCellAtlasData provided by the celldex package as the reference dataset. Our script is as follows.
library(dplyr)
library(Seurat) # Seurat version 5.0.1
library(celldex) # version version 1.12.0
library(SingleR) # SingleR version 2.4.1
pbmc.data <- Read10X(data.dir="pbmc3k_filtered_gene_bc_matrices\\filtered_gene_bc_matrices\\hg19", gene.column=1)
pbmc <- CreateSeuratObject(counts=pbmc.data, project="pbmc3k", min.cells=3, min.features=200)
pbmc[["percent.mt"]] <- PercentageFeatureSet(pbmc, pattern="^MT-")
pbmc <- NormalizeData(pbmc)
pbmc <- FindVariableFeatures(pbmc, selection.method="vst", nfeatures=2000)
all.genes <- rownames(pbmc)
pbmc <- ScaleData(pbmc, features=all.genes)
pbmc <- RunPCA(pbmc, features=VariableFeatures(object=pbmc))
pbmc <- FindNeighbors(pbmc, dims=1:10)
pbmc <- FindClusters(pbmc, resolution=0.5)
pbmc <- RunUMAP(pbmc, dims=1:10)
print(DimPlot(pbmc, reduction="umap"))
ref.data <- celldex::HumanPrimaryCellAtlasData(ensembl=TRUE)
results_main <- SingleR(test=as.SingleCellExperiment(pbmc), ref=ref.data, labels=ref.data$label.main)
results_fine <- SingleR(test=as.SingleCellExperiment(pbmc), ref=ref.data, labels=ref.data$label.fine)
pbmc$celltype_broad <- results_main$labels
pbmc$celltype_detailed <- results_fine$labels
print(DimPlot(pbmc, reduction="umap", group.by='celltype_broad', repel=T, label=TRUE))
print(DimPlot(pbmc, reduction="umap", group.by='celltype_detailed', repel=T, label=TRUE))
results_fine$labels_main = results_main$labels
write.table(results_fine, file="singler_results_without_clustering.txt", sep="\t", row.names=TRUE)
write.table(table(results_fine$labels), file="singler_results_without_clustering_summary.txt", sep="\t", row.names=TRUE)
We show the summary plot with the broad and detailed cell types identified by SingleR for the pbmc3K dataset here.
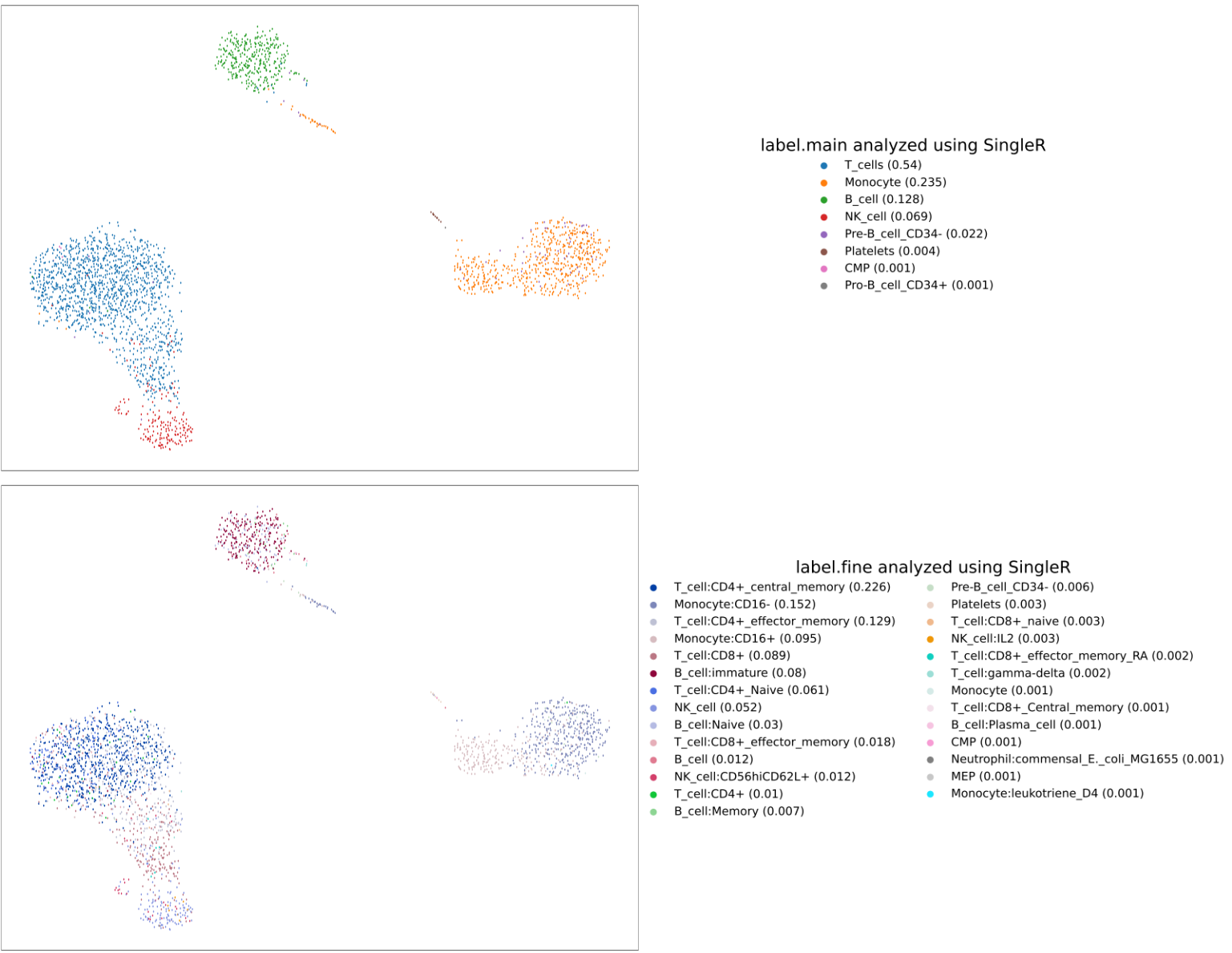
Comparing the results (CellKb vs SingleR)
You will notice that while the broad cell types are similar, CellKb has identified more detailed cell types than SingleR.
| Category | Name of the cell type in SingleR | Cell count | Name of the cell type in CellKb | Cell count |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| T cells (CD4+) | T_cell:CD4+_central_memory | 610 | central memory CD4 positive, alpha-beta T cell | 23 |
| T cells (CD4+) | T_cell:CD4+ | 28 | CD4-positive, alpha-beta T cell | 408 |
| T cells (CD4+) | T_cell:CD4+_effector_memory | 347 | effector memory CD4-positive, alpha-beta T cell | 156 |
| T cells (CD4+) | T_cell:CD4+_naive | 164 | naive thymus-derived CD4-positive, alpha-beta T cell | 23 |
| T cells (CD4+) | - | - | CD4-positive, alpha-beta memory T cell | 119 |
| T cells (CD4+) | - | - | CD4-positive helper T cell | 23 |
| T cells (CD4+) | - | - | CD4-positive, alpha-beta cytotoxic T cell | 11 |
| T cells (CD4+) | - | - | CD4-positive, CD25-positive, alpha-beta regulatory T cell | 4 |
| T cells (CD4+) | - | - | effector CD4-positive, alpha-beta T cell | 2 |
| T cells (CD4+) | - | - | T follicular helper cell | 2 |
| T cells (CD4+) | - | - | T-helper 1 cell | 2 |
| T cells (CD4+) | - | - | T-helper 17 cell | 2 |
| T cells (CD8+) | T_cell:CD8+ | 240 | CD8-positive, alpha-beta T cell | 94 |
| T cells (CD8+) | T_cell:CD8+_effector_memory | 48 | effector memory CD8-positive, alpha-beta T cell | 62 |
| T cells (CD8+) | T_cell:CD8+_naive | 9 | naive thymus-derived CD8-positive, alpha-beta T cell | 90 |
| T cells (CD8+) | T_cell:CD8+_effector_memory_RA | 5 | CD8-positive, alpha-beta memory T cell | 55 |
| T cells (CD8+) | T_cell:CD8+_central_memory | 4 | central memory CD8-positive, alpha-beta T cell | 30 |
| T cells (CD8+) | - | - | CD8-positive, alpha-beta cytotoxic T cell | 4 |
| T cells (CD8+) | - | - | effector CD8-positive, alpha-beta T cell | 4 |
| T cells (CD8+) | - | - | activated CD8-positive, alpha-beta T cell | 12 |
| T cells (CD8+) | - | - | effector memory CD8-positive, alpha-beta T cell, terminally differentiated | 2 |
| T cells (other) | T_cell:gamma-delta | 5 | gamma-delta T cell | 14 |
| T cells (other) | - | - | T cell | 102 |
| T cells (other) | - | - | mucosal invariant T cell | 82 |
| T cells (other) | - | - | regulatory T cell | 51 |
| T cells (other) | - | - | naive T cell | 50 |
| T cells (other) | - | - | exhausted T cell | 2 |
| T cells (other) | - | - | mature NK T cell | 20 |
| T cells (other) | - | - | immature NK T cell | 1 |
| T cells (other) | - | - | memory T cell | 1 |
| NK cells | NK_cell | 141 | natural killer cell | 162 |
| NK cells | NK_cell:CD56hiCD62L+ | 31 | CD16-negative, CD56-bright natural killer cell, human | 10 |
| NK cells | NK_cell:IL2 | 8 | mature NK T cell | 20 |
| NK cells | - | - | immature NK T cell | 1 |
| Monocytes | Monocyte:CD16- | 411 | classical monocyte | 117 |
| Monocytes | Monocyte:CD16+ | 259 | non-classical monocyte | 149 |
| Monocytes | Monocyte | 4 | monocyte | 320 |
| Monocytes | Monocyte:leukotriene_D4 | 1 | CD14-positive monocyte | 28 |
| Monocytes | - | - | CD14-low, CD16-positive monocyte | 25 |
| Monocytes | - | - | CD14-positive, CD16-positive monocyte | 4 |
| Monocytes | - | - | intermediate monocyte | 3 |
| B cells | B_cell:immature | 216 | - | |
| B cells | B_cell | 32 | B cell | 268 |
| B cells | B_cell:Naive | 82 | naive B cell | 39 |
| B cells | B_cell:Memory | 19 | memory B cell | 36 |
| B cells | B_cell:Plasma_cell | 4 | plasma cell | 3 |
| B cells | - | - | class switched memory B cell | 1 |
| Dendritic cells | - | - | conventional dendritic cell | 21 |
| Dendritic cells | - | - | dendritic cell | 19 |
| Dendritic cells | - | - | plasmacytoid dendritic cell | 3 |
| Platelets | Platelets | 9 | platelet | 21 |
| Platelets | - | - | megakaryocyte | 1 |
| Other | Pre-B_cell_CD34- | 17 | double negative thymocyte | 3 |
| Other | CMP | 4 | erythrocyte | 1 |
| Other | MEP | 1 | group 1 innate lymphoid cell | 1 |
| Other | Neutrophil:commensal_E._coli_MG1655 | 1 | lymphocyte | 1 |
| Other | - | - | progenitor cell | 1 |
We also notice that dendritic cells were incorrectly annotated by SingleR/celldex.

Conclusion
Thus, compared to SingleR, CellKb uses a large set of publications as a reference, and is able to identify cell types to a more detailed resolution.